Keys, Certificate and SSL/TLS
Public key & Secret key (or Private key)
Each person/company/entity has a key pair: public key and secret key.
- Public key:
- Can be shared all over the world, as an ID of its owner.
- Used to encrypt.
- Secret key:
- Keep it secret.
- Used to decrypt.
Uses in encryption
We have 2 persons:
- Alice:
PK_A&SK_A - Bob:
PK_B&SK_B
Alice want to send message msg to Bob, with encryption, only Bob can decrypts:
- Step 1: Alice encrypts message
msgwith Bob’s Public keyPK_B - Step 2: Alice send encrypted message to Bob
- Step 3: Bob decrypts message with Bob’s Private key
SK_B
What if Alice encrypts with Alice’s Private key, Bob decrypts with Alice’s Public Key?
=> Several issues:
- Any one can decrypts the message (any one can know Alice’s Public Key)
- This is actually called Signing process
Uses in Signing
Now Alice asks Bob to help her give non-secret message msg to Chris.
When received from Bob, how Chris knows if this is actually the message from Alice?
- Step 1: Alice signs the message
msgwith Alice’s Private keySK_A - Step 2: Bob handles signed message to Chris
- Step 3: Chris uses Alice’s Public key
PK_Ato decrypt and verifies the message from Alice
In the other words, by using this steps, we can authenticate the sender
Digital Signature
In above example, at step 1, when Alice signs the message, that action creates a Digital Signature
Attach that signature to a message, then we have a signed document:
Message + Signature = Signed Message
The example above can be reinterpret as:
- Step 1: Alice composes a
msg, sign it with her Secret keySK_A, which result asignature. - Step 2: Alice tell Bob to give that
msgandsignatureto Chris. - Step 3: Chris doesnt trust Bob, he want to confirm Alice actually signed on that doc.
Chris knows about Alice identity (Alice’sPK_A) and uses it to decryptssignature, to verify.
Note:
- Only you can sign (by secret key), any one can verify (by public key)
- Signature is tied to one document, different documents have different signature (but signed by same secret key).
Certificate & CA
A problem arises at Step 3 in above example.
How does Chris know PK_A is actually Alice identity?
What if David fooled Chris a long time ago, that David is Alice and David’s PK_A is Alice’s Public key?
So we need a trusted Certificate to prove the ownership of a Public Key..
And the trusted organization issues that Certificate, called CA (Certificate Authority)
Certificate
Certificate is an electronic document used to prove the ownership of a public key. Cert contains these info:
- Public key
- Identity info of the owner of that Public key
- Signature of CA on this document
Back to prior example, now Alice need to register for her certificate:
- Step 1: Alice sends her info + public key to CA
- Step 2: CA checks Alice and composes a cert, includes Alice’s info + public key
- Step 3: CA then sign that cert, with the CA’s Private Key
- Step 4: CA send back cert to Alice
Now, when Chris received Alice’s msg from Bob:
- Step 1: Chris asks CA for Alice’s certificate (assume Chris trusts this CA)
- Step 2: CA responses with Alice’s certificate
- Step 3: Chris get Alice’s Public Key from cert, uses it to verify
msgis actually from Alice
Practical examples
1. Android APK signing
Alice creates an Android app, first she builds into an APK file. At this point, this APK contains no information about
Alice, we call it unsigned APK.
Anyone has this APK can’t know if it’s really built by Alice or another person.
In fact, Android system prevents installation of this APK (error: unsigned package).
Signing APK file
- Step 1: Alice creates a key pair
- Step 2: Alice creates a Certificate includes: public key + the app info
- Step 3: Alice uses tool to attach Certificate into APK, which result a new Signed APK
In this example, we solved the issue of verifying an APK’s author.
Here we assume: first installation uses APK truly from Alice.
Later, when upgrading to newer APK version, we check that APK cert, it must match 1st APK certificate, mean also come
from Alice.
Q: Anyone can sign APK, how is this secured?
=> New APK must matches with cert from 1st installation.
Q: What if 1st APK is provided by faked Alice?
=> Then we’re fucked. But we should install 1st APK from trusted source only (Google Play). Then later APK versions
that from faked Alice will be detected.
Q: Can Alice’s cert be extracted from APK?
=> YES
Q: What if hacker use this cert to sign his malicious APK?
=> Then that APK becomes valid APK (from Alice). So we should install APK from trusted source only.
2. HTTPS
Suppose Alice and apple.com want to communicate secretly. This is how it can be setup (Source):
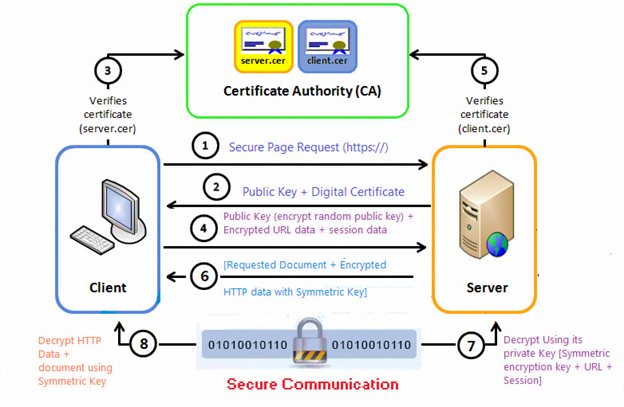
Key points:
- Client can verifies Server by checking with trust CA about Server’s cert
- After identities verification, both parties agreed to use Session key for data encryption
- Session key is only shared among Client and Server
- Without Session key, man-in-the-middle can’t read encrypted data
This is very good explanation: First few ms of HTTPS
Q: How to be sure that is trusted CA?
=> Trust chain - a chain of CA, ending at root CA.
- apple.com’s certificate is issued by CA1
- CA1’s certificate is issued by CA2 and so on until root CA
- Root CA’s certificate is trusted by browsers. It’s built-in
Q: What happens if DNS poisoning?
=> It depends
Suppose hacker poison our DNS, that point apple.com to malicious server IP address.
When we open browser and go to https://apple.com, there are 2 cases:
- The faked server sends real certificate of apple.com to browser
- Browser trusts that server is real (display green certified icon)
- Browser encrypts session key (with public key in cert), sends to server
- Server can’t decrypt session key, since server doesnt have private key of apple.com
- Communication ends here
- The faked server sends faked certificate to browser
- Browser failed to verify cert at root CA. Display red certificate icon and warning
- If we ignored browser warning, the communication continue as normal, and the attack succeed
Q: What if we dont use browser, but instead API or code?
=> In case 2 above, we’re fucked. So we should implement verify cert process.